Ground Engineering
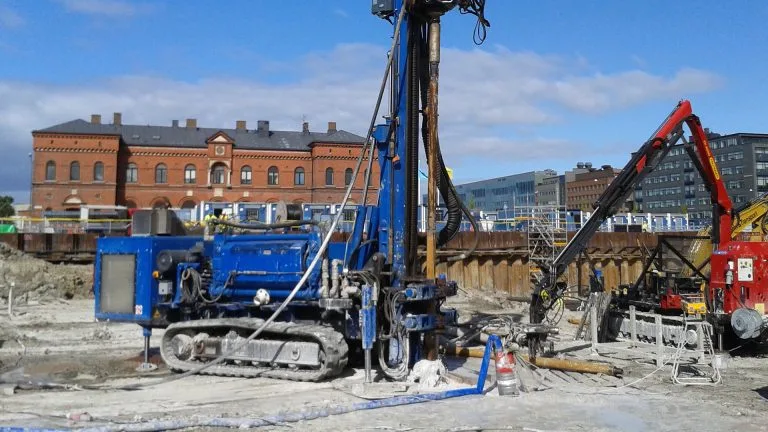
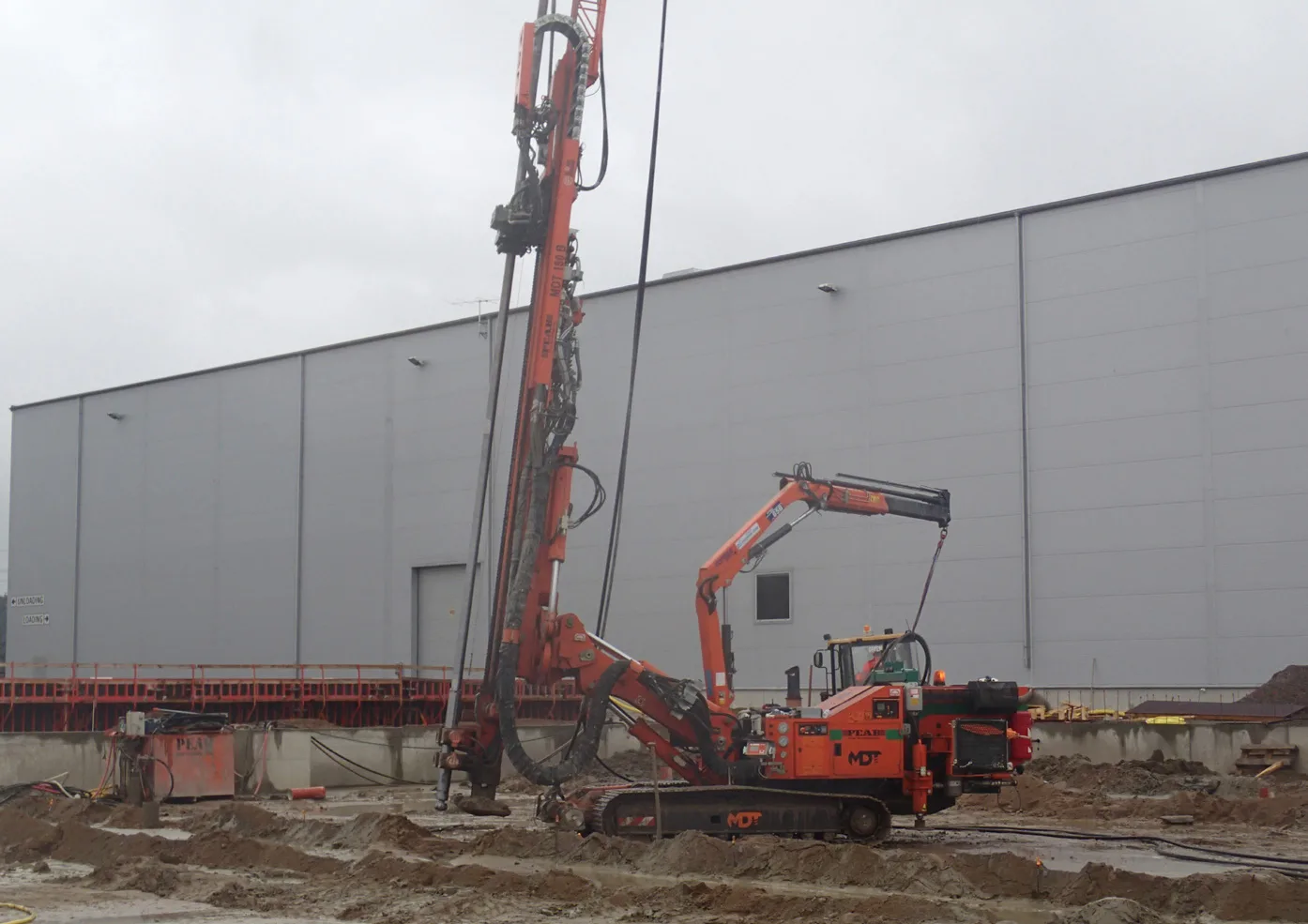
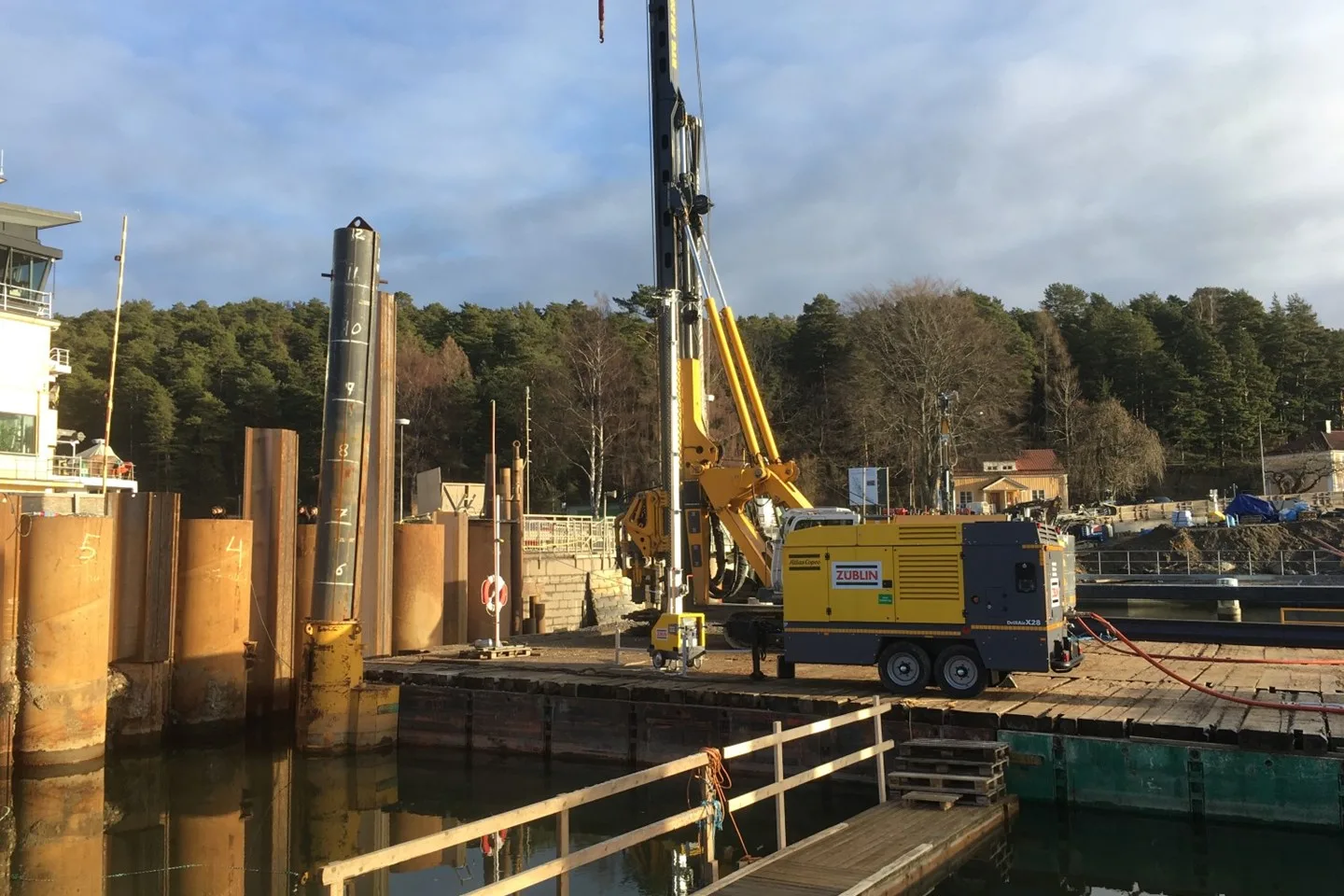
Our water-powered DTH hammer is capable of penetrating any formation while maintaining speed and straightness. Hard rock, boulders, concrete, lime stone, granite, till, water rich formations and dense clay.
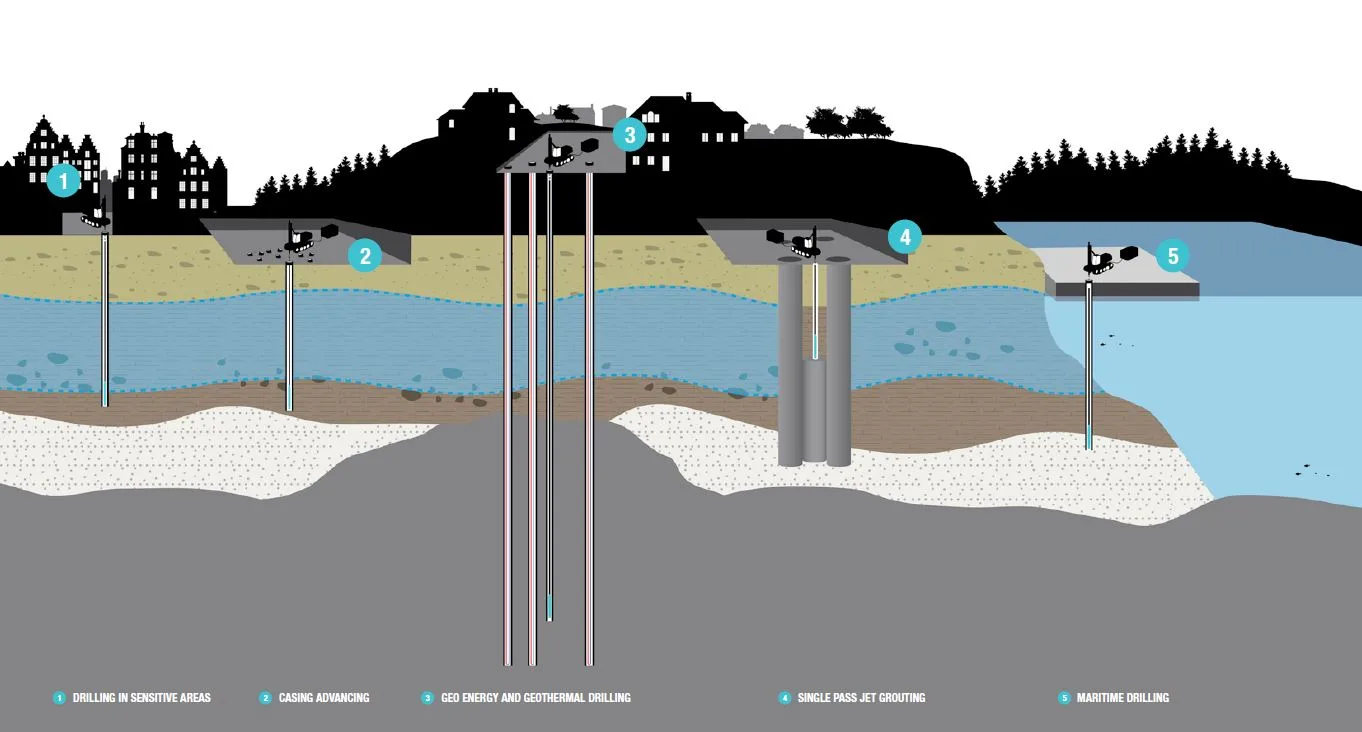
Case studies
See our featured Case studies below to learn what real world Ground Engineering-projects our technology has been a part of.



